BC639 Transistor NPN High Current
BC639 Transistor – NPN High Current (TO-92 Package)
Overview:
The BC639 is a high-current NPN bipolar junction transistor (BJT) designed for switching and linear amplification in medium-power electronic circuits. With a collector current rating of up to 1 ampere, the BC639 is ideal for controlling relays, motors, lamps, and other moderate loads from microcontrollers like Arduino, ESP32, or Raspberry Pi. Its compact TO-92 package makes it suitable for compact or breadboarded designs.
Key Features:
High collector current: Up to 1A continuous
Collector-emitter voltage: Up to 80V – handles moderate power loads
Gain (hFE): 40 to 250 – good amplification in switching mode
Fast switching: Useful in PWM and signal control circuits
Compatible with logic-level control from Arduino or other MCUs
Compact TO-92 package – easy to mount and prototype
Technical Specifications:
| Parameter | Value |
|---|---|
| Transistor Type | NPN |
| Package | TO-92 |
| Max Collector Current | 1A |
| Max Collector-Emitter Voltage | 80V |
| Max Collector-Base Voltage | 100V |
| Max Emitter-Base Voltage | 5V |
| DC Current Gain (hFE) | 40 – 250 |
| Max Power Dissipation | 1W @ 25°C |
| Transition Frequency | 100 MHz |
| Operating Temperature Range | -65°C to +150°C |
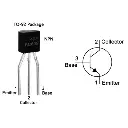
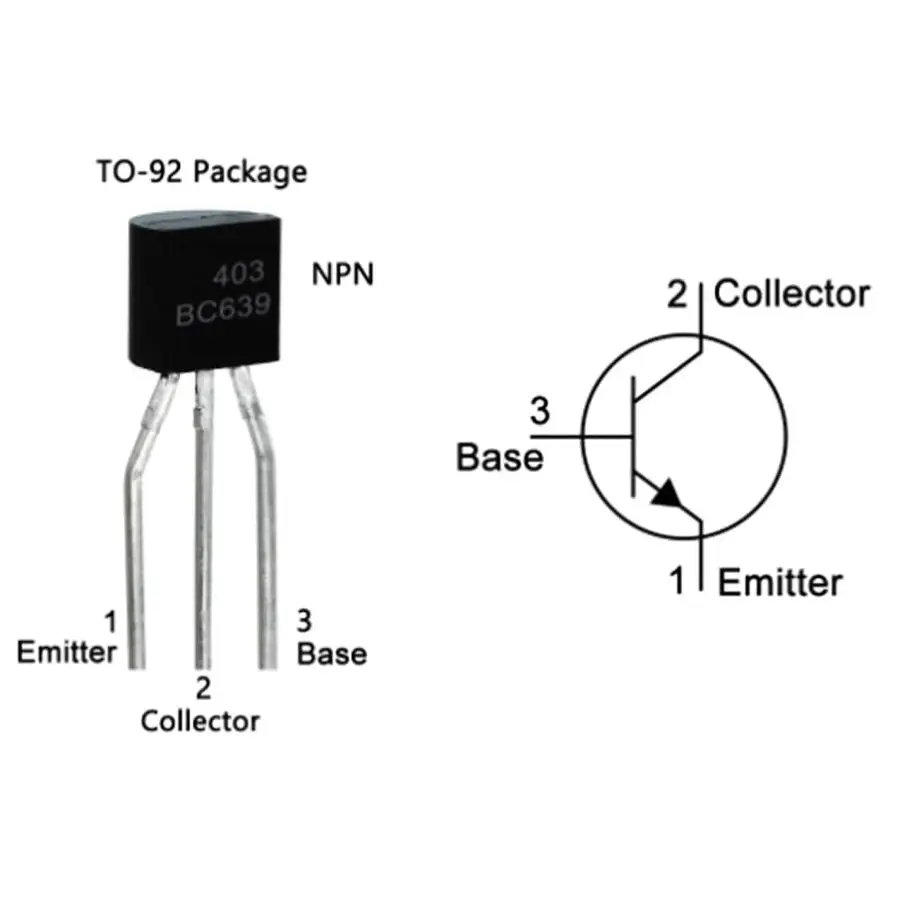
Pinout (TO-92 Package):
| Pin Number | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Collector | Connect to load or supply |
| 2 | Base | Input control (via resistor) |
| 3 | Emitter | Connect to ground (GND) |
Wiring with Arduino Uno (Example – Load Switching):
| Arduino Uno | BC639 Transistor |
|---|---|
| Digital Pin (e.g., D6) | Base (via 1kΩ resistor) |
| GND | Emitter |
| Load → VCC | Collector |
💡 Use a flyback diode across any inductive loads like motors or relays to protect the transistor.
Sample Code (Arduino):
CopyEditint transistorPin = 6; // Connects to base through 1k resistor void setup() { pinMode(transistorPin, OUTPUT); } void loop() { digitalWrite(transistorPin, HIGH); // Turn ON load delay(1000); digitalWrite(transistorPin, LOW); // Turn OFF load delay(1000); }
Applications:
Switching relays, motors, or solenoids
Driving high-current LEDs or lamps
Signal amplification in analog circuits
Level shifting between logic systems
General-purpose medium power control